| Version 58 (modified by , 20 months ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
GW16146 802.11ah HaLow Mini-PCIe Radio Module
The GW16146 is a miniPCIe form factor 802.11ah radio consisting of:
- FT232H MPSSE USB to SPI bridge
- Silex SX-NEWAH module based on Newracom NRC7292 (US only)
The GW16146 differs from the Newracom NRC7292 EVK in the following ways:
- Sits behind a FT232H USB to SPI bridge
- Uses software polling instead of an interrupt
- Uses the Silex SX-NEWAH radio containing the NRC7292 but RF tuned for US operation
View the GW16146 Product Page for pricing and specifications
802.11ah Showcase
View the Gateworks 802.11ah Showcase to learn more about 802.11ah
- 802.11ah High Client Count Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=exhCXCseYdk
- 802.11ah Range Testing Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y_qmCR1so2c
Features
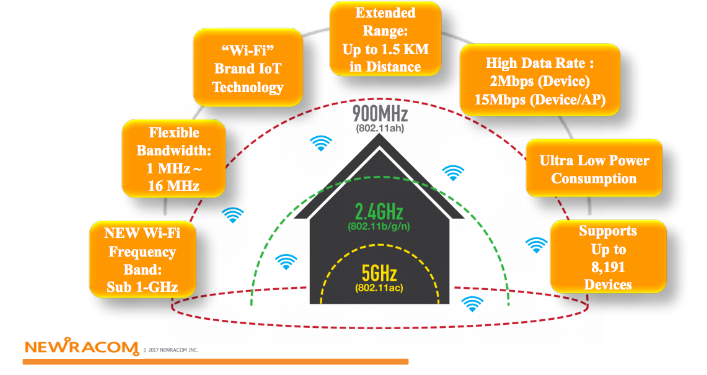
The Silex SX-NEWAH module featuring the Newracom 7292 features:
- IEEE 802.11ah operating in Sub 1GHz license-exempt band
- Offers a much greater range over 2.5GHz and 5GHz technologies
- Offers a much higher data rate than proprietary Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) technologies such as LoRa and Sigfox
- Full IP stack lowers barrier to entry over proprietary Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) technologies such as LoRa and Sigfox
- Latest generation Wi-Fi security - WPA3
- Channel widths: 1/2/4MHz channel widths with optional short guard interval (SGI) (yield 150Kbps to 15Mbps PHY throughput at the PHY layer but due to USB-to-SPI and driver polling maxes out at about 3-4.5mbps)
- Streams: 1 spatial stream
- Data rates: MCS0-MCS7, MCS10 (1MHz only)
- Client / Node count: 8,191 theoretical (no security). With security, it will be less due to memory limitations, but over 1000 clients have been confirmed working with security enabled.
- Country: US support only
- Modes: Infrastructure, Monitor. 802.11s mesh.
- Auth / Encryption: Open, WPA2-PSK(AES), WPA3-OWE, WPA3-SAE
- OFDM modulation
- AES-CCMP encryption
- 750 to 950MHz frequency band
- TX gain range: 23dB
- RX noise figure: <4dB
- Max input level: -10dBm
- Dual embedded ARM Cortex-M0 and Cortex-M3 processor
- SPI host interface
- Only 1 GW16146 is supported on a give system; as there is no concrete way to associate SPI bus number with particular device. The bus number assignment relies on USB bus scan and device probe sequence
RF transmitter specifications:
| BW | Freq (MHz) | Data Rates (MCS) | TX Power (min/typ/max dBm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1MHz | 903.5 ~ 915.5 | 0,1,2,3,4,10 | 20.5 / 23.0 / 25.5 |
| 5 | 19.5 / 22.0 / 24.5 | ||
| 6 | 15.5 / 18.0 / 20.5 | ||
| 7 | 11.5 / 14.0 / 16.5 | ||
| 916.5 ~ 926.5 | 0,1,2,3,4,10 | 19.5 / 22.0 / 24.5 | |
| 5 | 18.5 / 21.0 / 23.5 | ||
| 6 | 15.5 / 18.0 / 20.5 | ||
| 7 | 11.5 / 14.0 / 16.5 | ||
| 2MHz | 905 ~ 917 | 0,1,2,3,4 | 20.5 / 22.0 / 24.5 |
| 5 | 19.5 / 21.0 / 23.5 | ||
| 6 | 12.5 / 18.0 / 20.5 | ||
| 7 | 11.5 / 14.0 / 16.5 | ||
| 9195 ~ 925 | 0,1,2,3,4 | 19.5 / 22.0 / 24.5 | |
| 6 | 12.5 / 15.0 / 17.5 | ||
| 7 | 11.5 / 14.0 / 16.5 | ||
| 4MHz | 910 ~ 922 | 0,1,2,3,4,5 | 18.5 / 21.0 / 23.5 |
| 6 | 12.5 / 15.0 / 17.5 | ||
| 7 | 11.5 / 14.0 / 16.5 |
MCS
Modulation and coding schemes (for 1 spatial stream 1/2/4MHz channels):
| MCS index | Modulation and coding rate | 1MHz BW (mbps) | 2MHz BW (mbps) | 4MHz BW (mbps) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| long GI | short GI | long GI | short GI | long GI | short GI | ||
| 0 | BPSK 1/2 | 0.3 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 0.72 | 1.35 | 1.5 |
| 1 | QPSK 1/2 | 0.6 | 0.67 | 1.3 | 1.44 | 2.7 | 3.0 |
| 2 | QPSK 3/4 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.95 | 2.17 | 4.05 | 4.5 |
| 3 | 16-QAM 1/2 | 1.2 | 1.33 | 2.6 | 2.89 | 5.4 | 6.0 |
| 4 | 16-QAM 3/4 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 3.9 | 4.33 | 8.1 | 9.0 |
| 5 | 64-QAM 2/3 | 2.4 | 2.67 | 5.2 | 5.78 | 10.8 | 12.0 |
| 6 | 64-QAM 3/4 | 2.7 | 3.0 | 5.85 | 6.5 | 12.2 | 13.5 |
| 7 | 64-QAM 5/6 | 3.0 | 3.34 | 6.5 | 7.22 | 13.5 | 15.0 |
| 10 | BPSK 1/2 x 2 | 0.15 | 0.17 | - | - | - | - |
- See rate table at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.11ah
- These are maximum PHY data rates - actual throughput depends also on packet loss and most importantly SPI and USB bus overhead and latency which effectively reduces throughput of the GW16146 to a max of around 3-4.5mbps.
- Range is affected by BW used. 1MHz should be used for long range applications. See some example range by BW here: https://youtu.be/Y_qmCR1so2c?t=188
Receiver
RF receiver specifications:
| BW | Modulation | Data Rates | Rx Minimum Sensitivity (typ/max dBm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1MHz | BPSK | MCS10 | -104 / -98 |
| BPSK | MCS0 | -102 / -95 | |
| QPSK | MCS1 | -100 / -92 | |
| QPSK | MCS2 | -95 / -90 | |
| 16 QAM | MCS3 | -92 / -87 | |
| 16 QAM | MCS4 | -88 / -83 | |
| 64 QAM | MCS5 | -89 / -79 | |
| 64 QAM | MCS6 | -86 / -78 | |
| 64 QAM | MCS7 | -85 / -77 | |
| 2MHz | BPSK | MCS0 | -96 / -92 |
| QPSK | MCS1 | -96 / -89 | |
| QPSK | MCS2 | -94 / -87 | |
| 16 QAM | MCS3 | -92 / -84 | |
| 16 QAM | MCS4 | -88 / -80 | |
| 64 QAM | MCS5 | -84 / -76 | |
| 64 QAM | MCS6 | -83 / -75 | |
| 64 QAM | MCS7 | -81 / -74 | |
| 4MHz | BPSK | MCS0 | -92 / -89 |
| QPSK | MCS1 | -92 / -86 | |
| QPSK | MCS2 | -92 / -84 | |
| 16 QAM | MCS3 | -88 / -81 | |
| 16 QAM | MCS4 | -85 / -77 | |
| 64 QAM | MCS5 | -81 / -73 | |
| 64 QAM | MCS6 | -80 / -72 | |
| 64 QAM | MCS7 | -78 / -71 |
Channel Mapping
Channel Mapping (US):
- The SX-NEWAH Channel Mapping application note from Silex states the frequency range is 903.5 MHz to 926.5 MHz supporting channel widths of 1MHz, 2MHz, or 4MHz. The channel map (differs a bit from Newracom's info due to US) is:
- 1 MHz Wide channel mappings:
| Wi-Fi channel setting | Sub 1 GHz frequency [MHz] |
|---|---|
| 3 | 903.5 |
| 5 | 904.5 |
| 7 | 905.5 |
| 9 | 906.5 |
| 11 | 907.5 |
| 36 | 908.5 |
| 37 | 909.5 |
| 38 | 910.5 |
| 39 | 911.5 |
| 40 | 912.5 |
| 41 | 913.5 |
| 42 | 914.5 |
| 43 | 915.5 |
| 44 | 916.5 |
| 45 | 917.5 |
| 46 | 918.5 |
| 47 | 919.5 |
| 48 | 920.5 |
| 149 | 921.5 |
| 150 | 922.5 |
| 151 | 923.5 |
| 152 | 924.5 |
| 100 1 | 925.5 |
| 104 1 | 926.5 |
- use of these channels is not recommended as these are Clear Access Channels (CAC) which when used will takea full 60 seconds before they are operational
- 2 MHz Wide channel mappings:
| Wi-Fi channel setting | Sub 1 GHz frequency [MHz] |
|---|---|
| 6 | 905 |
| 10 | 907 |
| 153 | 909 |
| 154 | 911 |
| 155 | 913 |
| 156 | 915 |
| 157 | 917 |
| 158 | 919 |
| 159 | 921 |
| 160 | 923 |
| 161 | 925 |
- 4 MHz Wide channel mappings:
| Wi-Fi channel setting | Sub 1 GHz frequency [MHz] |
|---|---|
| 162 | 910 |
| 163 | 914 |
| 164 | 918 |
| 165 | 922 |
Antenna
This radio requires an antenna properly tuned for the target frequency.
Silex Recommended Antennas on Digi-Key:
- ethertronics X9000984-4GDSMB https://www.digikey.com/en/products/detail/kyocera-avx/X9000984-4GDSMB/13982460
- PSA (Walsin) RFDPA131000SMRB801 https://www.digikey.com/en/products/detail/walsin-technology-corporation/RFDPA131000SMRB801/12525199
Silex Recommended Antennas:
Gateworks sells a 900 MHz antenna, the GW10124. This antenna is *NOT* pre-certified by Silex, thus should only be used for development and will require re-certification.
- GW10124 Antenna Purchase the GW10124 Note antenna adapter cable not included
- Requires GW10036 u.FL to SMA Cable Adapter
Documentation
There are a number of documents in the Newracom nrc7292 driver repository which may prove useful:
- AN-7292-002-Dynamic Vendor IE.pdf
- AN-7292-007-11s_mesh_network.pdf
- UG-7292-002-Host%20driver%20porting.pdf
- UG-7292-007-Commnad%20line%20application.pdf
- UG-7292-011-NewraPeek.pdf
- UG-7292-015-Transmit_Power_Control.pdf
- Note that some of these documents are heavily tailored to the Newracom NRC7292 EVK which may differ in some ways to the GW16146
Other references:
- Silex SX-NEWAH product page - contains various specs and documents
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.11ah
Software
Software support consists of the following items: (This a summary. Details are below)
- Linux kernel driver for FT232H as a USB to SPI bridge on the GW16146
- Linux kernel driver for the NRC7292 SPI Radio chip
- Firmware files required for NRC7292 driver in /lib/firmware: nrc7292_cspi.bin and nrc7292_bd.dat
- Userspace cli_app application to performing miscellaneous configuration via Netlink to the NRC7292 driver
The above software support is present in the following:
- Venice Ubuntu Jammy (22.04) pre-built images
- Newport Ubuntu Focal (20.04) pre-built images.
- Ventana Ubuntu Focal (20.04) pre-built images
FT232H USB to SPI bridge
The FT232H features an multi-protocol engine that can be used for UART, JTAG, SPI, I2C among perhaps other things. The FT232H's MPSSE is great for generating signals to communicate using the SPI protocol. The MPSSE can take care of generating a clock signal from about 450hz to 30Mhz, and read & write bytes of data at that frequency.
Gateworks has programmed the USB VID:PID on the GW16146 to 0x2beb:0x0146 which binds to the out-of-tree Linux kernel spi-ft232h driver.
When a GW16146 is found on the USB bus a SPI master host controller will be registered with the Linux kernel (which you can see in /sys/class/spi_master) as well as registers a nrc80211 SPI device which binds to the nrc7292 driver. Note that earlier versions of this driver required you to manually determine the SPI bus and manually probe the nrc driver with arguments pointing to the bus. Please make sure you are using the latest version of these drivers (available on the Gateworks pre-built Ubuntu based OS images) to avoid this (or refer to earlier documentation).
Building:
- The driver compiles a single module 'spi-ft232h.ko' and can be built out-of-tree by assigning KDIR to the directory of your kernel:
KDIR=/usr/src/venice/bsp/linux make
NRC7292 kernel driver
The Silex SX-NEWAH module on the GW16146 has a Newracom NRC7292 which is supported by Newracom's open-source driver.
The Gateworks nrc7292 driver has some modifications to the Newracom NRC7292 driver:
- add support for v6.2+
- nrc-init: default to spi polling
- nrc-hif-cspi: remove spam from spi_check_ready
- nrc-mac80211: display wlan device registered
- nrc: add display of driver version and chip identified
- nrc: remove prints for non-errors
nrc7292 driver history:
- v1.5 (Oct 2023) - Gateworks now supports this
- v1.4 (June 2023) - Gateworks did not use this version of the driver
- v1.3 (April 2021) - Gateworks original driver
There is a large set of kernel params (which you can see via 'modinfo nrc.ko') but for our purposes the following are needed:
- fw_name - firmware file from /lib/firmware
- bd_name - Board data file from /lib/firmware
- spi_polling_interval - SPI polling interval in ms (recommend 5ms)
Example module loading:
modprobe nrc fw_name=nrc7292_cspi.bin bd_name=nrc7292_bd.dat spi_polling_interval=5
When using an OS like Ubuntu you create a file in /etc/modprobe.d/ to use these automatically when the module is loaded:
cat << EOF > /etc/modprobe.d/nrc.conf options nrc fw_name=nrc7292_cspi.bin bd_name=nrc7292_bd.dat spi_polling_interval=5 EOF
To find the correct wlan interface that is bound to the NRC7292 driver you can look at the devices in /sys/class/net to see which ones have a SPI based device-driver:
WLAN="$(for i in $(ls -d /sys/class/net/wlan* 2>/dev/null); do if [ -d $i/device/driver/spi* ]; then basename $i; fi; done)" echo $WLAN # wlan0
After bringing up the interface you can perform more configuration on it via the 'cli_app' (see below)
ifconfig $WLAN up
Building:
- The driver compiles a single module 'nrc.ko' and can be built out-of-tree by assigning KDIR to the directory of your kernel:
KDIR=/usr/src/venice/bsp/linux make
- Kernel Requirements: CONFIG_CRYPTO_CCM, CONFIG_CRYPTO_GCM, CONFIG_CRYPTO_SEQIV, CONFIG_CRYPTO_CBC, CONFIG_CRYPTO_CTR, CONFIG_CRYPTO_ECB, CONFIG_CRYPTO_AES
OpenWrt Information
For customers interested in OpenWRT, view repository link for NRC7292:
cli_app
There is a 'cli_app' that is part of the driver code which communicates with the driver via the Netlink generic socket family API. Netlink is a Linux kernel interface used for inter-process communication between kernel and userspace similar to unix domain sockets designed for transferring miscellaneous networking information between kernel space and userspace processes. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Netlink for details.
The cli_app facilitates setting misc details that are not handled via iw. The app can be used in interactive mode by running without args or by sending commands.
Example usage showing useful features:
- interactive mode
# ./cli_app =================================================== Newracom Command Line Application (2.4) =================================================== NRC> help =================================================================================================== help :show CLI tree exit :exit program show version :show version show config [vif_id] :show configuration show edca :show EDCA parameters show uinfo [vif_id] :show UMAC information show ampdu [clear] :show/clear AMPDU count show signal [start|stop] [interval] [number] :show rssi/snr show maxagg :show max aggregation show duty :show duty cycle show autotxgain :show autotxgain show cal_use :show cal_use show bdf_use :show board data use show recovery stats :show recovery show detection stats :show detection show temp :show temp show wakeup_pin :show wakeup pin configuration show wakeup_source :show wakeup source configuration show stats simple_rx :show received packet information show mac clear :clear TX/RX Statistics show mac tx stats :show TX Statistics show mac tx clear :clear TX Statistics show mac rx stats :show RX Statistics show mac rx clear :clear RX Statistics set gi <short|long|auto> :set guard interval set maxagg <AC(0-3)> <Max(0-13,0:off)> {size:default=0}:set aggregation set config <ack[0,1]> <agg[0,1]> <mcs> :set ack, aggregation, mcs set rc <on|off> [vif_id] [mode] :set rate control set duty <on|off> {duty window} {tx duration} {exclude mgmt[0|1]}:set duty cycle set cal_use <on|off> :set cal_use set bdf_use <on|off> :set board data use set txpwr <value(1~30)> :set txpwrt set wakeup_pin {Debounce:on|off} {PIN Number:0~31} :set wakeup pin for deepsleep set wakeup_soruce rtc gpio hspi :set wakeup source for deepsleep set addba [tid] {mac address} :set addba tid / send addba with mac address set delba [tid] {mac address} :set delba tid / send delba with mac address set rts <on|off|default> <threshold> <vif_id> :set rts on/off test mcs <mcs value> :set mcs test country JP <CS time> <Blank time> or <show> :set/show tx time control for JP(Japan) =================================================================================================== OK NRC> exit =================================================== Exit Newracom Command Line Application ===================================================
- Show software/hardware version info:
# ./cli_app show version Newracom Firmware Version : 01.03.03 gerrit/master : c977f Board Revision : 7292A OK
- Set use of board data for tx power levels and calibration:
# ./cli_app set bdf_use on Board Data use : on OK - Enable A-MPDU (frame aggregation):
# ./cli_app set maxagg 1 8 -------------------------------- updated aggregation ---------------------------------- AC : BK State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : BE State : ON Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : VI State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : VO State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- OK root@focal-venice-sta:~# ./cli_app set maxagg 1 on -------------------------------- updated aggregation ---------------------------------- AC : BK State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : BE State : ON Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : VI State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : VO State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- OK
- Set guard band interval to long (or short if you wish)
# ./cli_app set gi long guard interval : long OK - Enable RF calibration:
# ./cli_app set cal_use on Calibration_use : on Country : US OK
For more info see UG-7292-007-Command line application.pdf
Note that the interface needs to be up.
Configuration and Usage examples
Standard Configuration
Steps 1 through 4 below are required for operation:
- Set the country code (required for newer versions of the driver) (MANDATORY every boot)
iw reg set US- note that this can be done automatically in a number of ways:
- kernel cmdline: add 'cfg80211.ieee80211_regdom=US' to bootargs
- Ubuntu modprobe.d: 'echo "options cfg80211 ieee80211_regdom=US" > /etc/modprobe.d/cfg80211_regdomain.conf'
- OpenWrt modules.d: 'echo "cfg80211 ieee80211_regdom=US" > /etc/modules.d/cfg80211_regdomain.conf'
- note that this can be done automatically in a number of ways:
- Confirm the device exists on the USB bus:
lsusb shows GW16046 on bus with VID:0x2beb and PID=0x0146
lsusb -d 0x2beb:0x0146
# Bus 001 Device 003: ID 2beb:0146
- Find the correct wlan interface that is bound to the NRC7292 driver by looking for a devices in /sys/class/net with a SPI based device-driver:
WLAN="$(for i in $(ls -d /sys/class/net/wlan* 2>/dev/null); do if [ -d $i/device/driver/spi* ]; then basename $i; fi; done)" echo $WLAN # wlan0
- Bring up the interface (required for configuration below)
ifconfig $WLAN up - Now configure wlan0 as an access point or client (station) given different examples below.
Manual Configuration
Optional More Manual Config When Not Using Gateworks Ubuntu BSP:
- Confirm the device exists on the USB bus:
lsusb shows GW16046 on bus with VID:0x2beb and PID=0x0146
lsusb -d 0x2beb:0x0146
# Bus 001 Device 003: ID 2beb:0146
- Device Drivers: (this is done automatically when using the latest Gateworks Ubuntu BSP)
- Load the NRC7292 driver providing the fw_name bd_name and spi_polling_interval parameters:
modprobe nrc fw_name=nrc7292_cspi.bin bd_name=nrc7292_bd.dat spi_polling_interval=5
- After several seconds you should see a new wlan device under /sys/class/net
- Find the correct wlan interface that is bound to the NRC7292 driver by looking for a devices in /sys/class/net with a SPI based device-driver:
WLAN="$(for i in $(ls -d /sys/class/net/wlan* 2>/dev/null); do if [ -d $i/device/driver/spi* ]; then basename $i; fi; done)" echo $WLAN # wlan0
- Set the country code (required for newer versions of the driver) (MANDATORY every boot)
iw reg set US - bring up the interface (required for configuration below)
ifconfig $WLAN up
Popular CLI_APP Configuration
(Optional) Configure miscellaneous parameters via cli_app Netlink tool
- Enable transmission power controL (TPC)
# cli_app set bdf_use on # enable transmission power control (TPC) Board Data use : on OK - Configure frame aggregation
# cli_app set maxagg 1 8 # configure frame aggregation -------------------------------- updated aggregation ---------------------------------- AC : BK State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : BE State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : VI State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : VO State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- OK # cli_app set maxagg 1 on # enable frame aggregation -------------------------------- updated aggregation ---------------------------------- AC : BK State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : BE State : ON Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : VI State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 AC : VO State : OFF Value : 8 Size : 0 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- OK
- The Access Category (BK/BE/VI/VO) are based on ToS field in an IP header:
- BK: 0x20, 0x28, 0x38, 0x48, 0x58
- BE: 0x00, 0x60, 0x70
- VI: 0x88, 0x90, 0x98, 0xa0, 0xb8
- VO: 0xc0, 0xe0
- The Access Category (BK/BE/VI/VO) are based on ToS field in an IP header:
- configure guard band interval
# cli_app set gi long # set long guard interval guard interval : long OK - Configure power calibration
# cli_app set cal_use on # enable power calibration Calibration_use : on Country : US OK - For the Command Line App usage details see UG-7292-007-Command Line Application.pdf
Access Point / Client Station Examples
- Configure AP (access point) or STA (station / client) mode:
- Define your channel and SSID via env variables (used in scripts below)
SSID=halow_demo CH=161 PSK=12345678
- For Channel mapping details see: UG-7292-003-S1G_Channel.pdf
- Open security model:
- AP (access point) (using WLAN/SSID/CH env variables)
# apt install hostapd # make sure hostapd is installed # /etc/init.d/hostapd stop # make sure its not running # cat << EOF > /tmp/hostapd.conf ctrl_interface=/var/run/hostapd country_code=US interface=$WLAN ssid=$SSID hw_mode=a channel=$CH ieee80211h=1 ieee80211d=1 ieee80211n=1 macaddr_acl=0 driver=nl80211 beacon_int=100 ap_max_inactivity=16780 EOF # hostapd /tmp/hostapd.conf & [1] 1006 Configuration file: /tmp/hostapd.conf rfkill: Cannot open RFKILL control device wlan0: interface state UNINITIALIZED->COUNTRY_UPDATE Using interface wlan0 with hwaddr 84:25:3f:87:fc:b6 and ssid "halow_demo" wlan0: interface state COUNTRY_UPDATE->ENABLED wlan0: AP-ENABLED
- STA (station / client) (using WLAN/SSID env variables)
# cat << EOF > /tmp/wpa_supplicant.conf ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant country=US network={ ssid="$SSID" scan_ssid=1 key_mgmt=NONE freq_list=2412 2422 2432 2442 2452 2462 5180 5185 5190 5195 5200 5205 5210 5215 5220 5225 5230 5235 5240 5745 5750 5755 5760 5500 5520 5540 2417 2437 2457 5765 5770 5775 5780 5785 5790 5795 5800 5805 5560 2447 5810 5815 5820 5825 5580 scan_freq=2412 2422 2432 2442 2452 2462 5180 5185 5190 5195 5200 5205 5210 5215 5220 5225 5230 5235 5240 5745 5750 5755 5760 5500 5520 5540 2417 2437 2457 5765 5770 5775 5780 5785 5790 5795 5800 5805 5560 2447 5810 5815 5820 5825 5580 } p2p_disabled=1 EOF # wpa_supplicant -i $WLAN -c /tmp/wpa_supplicant.conf &
- AP (access point) (using WLAN/SSID/CH env variables)
- WPA2-PSK security
- AP (using WLAN/SSID/CH/PSK env variables)
# cat << EOF > /tmp/hostapd.conf ctrl_interface=/var/run/hostapd country_code=US interface=$WLAN ssid=$SSID hw_mode=a channel=$CH ieee80211h=1 ieee80211d=1 ieee80211n=1 macaddr_acl=0 driver=nl80211 beacon_int=100 ap_max_inactivity=16780 wpa=2 wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK wpa_pairwise=CCMP rsn_pairwise=CCMP wpa_passphrase=$PSK EOF # hostapd /tmp/hostapd.conf &
- STA (station / client) (using WLAN/SSID/PSK env variables)
# cat << EOF > /tmp/wpa_supplicant.conf ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant country=US update_config=1 network={ ssid="$SSID" scan_ssid=1 proto=RSN key_mgmt=WPA-PSK pairwise=CCMP group=CCMP psk="$PSK" freq_list=2412 2422 2432 2442 2452 2462 5180 5185 5190 5195 5200 5205 5210 5215 5220 5225 5230 5235 5240 5745 5750 5755 5760 5500 5520 5540 2417 2437 2457 5765 5770 5775 5780 5785 5790 5795 5800 5805 5560 2447 5810 5815 5820 5825 5580 scan_freq=2412 2422 2432 2442 2452 2462 5180 5185 5190 5195 5200 5205 5210 5215 5220 5225 5230 5235 5240 5745 5750 5755 5760 5500 5520 5540 2417 2437 2457 5765 5770 5775 5780 5785 5790 5795 5800 5805 5560 2447 5810 5815 5820 5825 5580 } p2p_disabled=1 ignore_old_scan_res=1 EOF # wpa_supplicant -i $WLAN -c /tmp/wpa_supplicant.conf &
- AP (using WLAN/SSID/CH/PSK env variables)
- WPA3-SEA (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simultaneous_Authentication_of_Equals)
- AP (using WLAN/SSID/PSK env variables)
# cat << EOF > /tmp/hostapd.conf ctrl_interface=/var/run/hostapd country_code=US interface=$WLAN ssid=$SSID hw_mode=a channel=$CH ieee80211h=1 ieee80211d=1 ieee80211n=1 ieee80211w=2 macaddr_acl=0 driver=nl80211 beacon_int=100 ap_max_inactivity=16780 wpa=2 wpa_key_mgmt=SAE wpa_pairwise=CCMP rsn_pairwise=CCMP wpa_passphrase=$PSK EOF # hostapd /tmp/hostapd.conf &
- STA (station / client) (using WLAN/SSID/PSK env variables)
# cat << EOF > /tmp/wpa_supplicant.conf ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant country=US update_config=1 network={ ssid="$SSID" scan_ssid=1 proto=RSN key_mgmt=SAE pairwise=CCMP group=CCMP psk="$PSK" ieee80211w=2 freq_list=2412 2422 2432 2442 2452 2462 5180 5185 5190 5195 5200 5205 5210 5215 5220 5225 5230 5235 5240 5745 5750 5755 5760 5500 5520 5540 2417 2437 2457 5765 5770 5775 5780 5785 5790 5795 5800 5805 5560 2447 5810 5815 5820 5825 5580 scan_freq=2412 2422 2432 2442 2452 2462 5180 5185 5190 5195 5200 5205 5210 5215 5220 5225 5230 5235 5240 5745 5750 5755 5760 5500 5520 5540 2417 2437 2457 5765 5770 5775 5780 5785 5790 5795 5800 5805 5560 2447 5810 5815 5820 5825 5580 } p2p_disabled=1 ignore_old_scan_res=1 EOF # wpa_supplicant -i $WLAN -c /tmp/wpa_supplicant.conf &
- AP (using WLAN/SSID/PSK env variables)
- WPA3-OWE (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Opportunistic_Wireless_Encryption)
- AP (using WLAN/SSID/PSK env variables)
# cat << EOF > /tmp/hostapd.conf ctrl_interface=/var/run/hostapd country_code=US interface=$WLAN ssid=$SSID hw_mode=a channel=$CH ieee80211h=1 ieee80211d=1 ieee80211n=1 ieee80211w=2 macaddr_acl=0 driver=nl80211 beacon_int=100 ap_max_inactivity=16780 wpa=2 wpa_key_mgmt=OWE wpa_pairwise=CCMP rsn_pairwise=CCMP EOF # hostapd /tmp/hostapd.conf &
- STA (using WLAN/SSID/PSK env variables)
# cat << EOF > /tmp/wpa_supplicant.conf ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant country=US update_config=1 pmf=2 network={ ssid="$SSID" scan_ssid=1 proto=RSN key_mgmt=OWE pairwise=CCMP group=CCMP psk="$PSK" ieee80211w=2 freq_list=2412 2422 2432 2442 2452 2462 5180 5185 5190 5195 5200 5205 5210 5215 5220 5225 5230 5235 5240 5745 5750 5755 5760 5500 5520 5540 2417 2437 2457 5765 5770 5775 5780 5785 5790 5795 5800 5805 5560 2447 5810 5815 5820 5825 5580 scan_freq=2412 2422 2432 2442 2452 2462 5180 5185 5190 5195 5200 5205 5210 5215 5220 5225 5230 5235 5240 5745 5750 5755 5760 5500 5520 5540 2417 2437 2457 5765 5770 5775 5780 5785 5790 5795 5800 5805 5560 2447 5810 5815 5820 5825 5580 } p2p_disabled=1 ignore_old_scan_res=1 EOF # wpa_supplicant -i $WLAN -c /tmp/wpa_supplicant.conf &
- AP (using WLAN/SSID/PSK env variables)
- Define your channel and SSID via env variables (used in scripts below)
802.11s Mesh
Mesh has a lot of options and is complex in it's nature.
Newracom uses and evaluation kit (EVK) on a Raspberry Pi and a lot of mesh functionality and examples about that are shown in this document here . Gateworks does not use a lot of the scripts and software packages from Newracom despite using the Newracom driver.
A basic example to setup a 'mesh point' would be the following:
- Verify proper operation of the GW16146 in standard AP/STA mode first
- Create a wpa_supplicant.conf file that defines the radio as a 'mesh point', example below of a wpa_supplicant.conf file
ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant country=US network={ ssid="nrc_mesh" mode=5 scan_ssid=1 key_mgmt=NONE beacon_int=100 #BW.11ah(Freq) frequency=5795 freq_list=5795 scan_freq=5795 dot11MeshRetryTimeout=1000 dot11MeshHoldingTimeout=400 dot11MeshMaxRetries=4 mesh_rssi_threshold=-90 mesh_basic_rates= 60 120 240 #no_auto_peer=1 } p2p_disabled=1 ignore_old_scan_res=1 mesh_max_inactivity=-1 - Be sure the wlan0 interface exists and is up
ifconfig wlan0 up
- Bring up the radio using wpa_supplicant:
wpa_supplicant -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf -dddd &
Verify that the interface is in 'mesh' mode by seeing where it says 'type mesh point' in the example below:
root@mesh-10-3:~# iw wlan0 info
Interface wlan0
ifindex 4
wdev 0x1
addr 1c:bc:ec:1b:2a:87
type mesh point
wiphy 0
channel 159 (5795 MHz), width: 20 MHz, center1: 5795 MHz
txpower 30.00 dBm
multicast TXQ:
qsz-byt qsz-pkt flows drops marks overlmt hashcol tx-bytes tx-packets
0 0 28 0 0 0 0 2816 28
Show and 'dump' a list of all connected mesh nodes:
root@mesh-10-3:~# iw wlan0 station dump Station 84:25:3f:87:fc:b6 (on wlan0) inactive time: 17700 ms rx bytes: 287288 rx packets: 3921 tx bytes: 869 tx packets: 13 tx retries: 0 tx failed: 0 rx drop misc: 11 signal: -90 dBm signal avg: -90 dBm Toffset: 1596110650506024084 us tx bitrate: 6.0 MBit/s tx duration: 0 us rx bitrate: 6.0 MBit/s rx duration: 0 us expected throughput: 2.929Mbps mesh llid: 0 mesh plid: 0 mesh plink: ESTAB mesh airtime link metric: 2731 mesh connected to gate: no mesh connected to auth server: no mesh local PS mode: ACTIVE mesh peer PS mode: ACTIVE mesh non-peer PS mode: ACTIVE authorized: yes authenticated: yes associated: yes preamble: long WMM/WME: yes MFP: no TDLS peer: no DTIM period: 2 beacon interval:100 connected time: 203 seconds associated at [boottime]: 23.826s associated at: 1700600258324 ms current time: 1700600460874 ms Station 1c:bc:ec:1b:2a:87 (on wlan0) inactive time: 360 ms rx bytes: 287878 rx packets: 3927 tx bytes: 1541 tx packets: 17 tx retries: 0 tx failed: 0 rx drop misc: 13 signal: -84 dBm signal avg: -84 dBm tx bitrate: 6.0 MBit/s tx duration: 0 us rx bitrate: 6.0 MBit/s rx duration: 0 us expected throughput: 8.789Mbps mesh llid: 0 mesh plid: 0 mesh plink: ESTAB mesh airtime link metric: 911 mesh connected to gate: no mesh connected to auth server: no mesh local PS mode: ACTIVE mesh peer PS mode: ACTIVE mesh non-peer PS mode: ACTIVE authorized: yes authenticated: yes associated: yes preamble: long WMM/WME: yes MFP: no TDLS peer: no DTIM period: 2 beacon interval:100 connected time: 203 seconds associated at [boottime]: 23.836s associated at: 1700600258334 ms current time: 1700600460875 ms root@mesh-10-3:~#
Show and 'dump' a path of all connected mesh nodes: (example shows to get to node 84:25:3f:87:fc:b6, you will need to 'hop' through 1c:bc:ec:1b:2a:87, thus proving the mesh is working)
root@mesh-10-3:~# iw wlan0 mpath dump DEST ADDR NEXT HOP IFACE SN METRIC QLEN EXPTIME DTIM DRET FLAGS HOP_COUNT PATH_CHANGE 1c:bc:ec:1b:2a:87 1c:bc:ec:1b:2a:87 wlan0 0 911 0 0 0 0 0x10 1 1 84:25:3f:87:fc:b6 1c:bc:ec:1b:2a:87 wlan0 4 1017 0 0 0 0 0x14 2 4
To start mesh on every boot, a system service (read more on google) can be setup or a simple /etc/rc.local script like so:
sleep 2s iw reg set US && ifconfig wlan0 up && ifconfig eth0 down && ifconfig wlan0 192.168.10.3 sleep 2s wpa_supplicant -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf -dddd & exit 0
Adhoc / IBSS Mode
Adhoc / IBSS Mode may only be supported with specific driver versions
Troubleshooting
- Ensure the device can be seen on the USB bus:
# lsusb -d 0x2beb:0x0146 Bus 001 Device 003: ID 2beb:0146
- Ensure the spi_ft232h driver is loaded
# lsmod | grep ft232 spi_ft232h 24576 0 # dmesg | grep ft232 [ 7.555554] usbcore: registered new interface driver spi_ft232h
- Ensure the spi_ft232h driver has registers a SPI bus:
# ls -l /sys/class/spi_master/ | grep ft232h lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Aug 31 20:13 spi3 -> ../../devices/platform/soc@0/soc@0:bus@32c00000/32e50000.usb/ci_hdrc.1/usb1/1-1/1-1.3/1-1.3:1.0/spi-ft232h.0/spi_master/spi3
- Ensure the there is a wireless interface in /sys/class/net:
# ls /sys/class/net eth0 eth1 lo wlan0 - Possible regulatory domain issue:
Because there is not country set in the target, the target asserts. As was shown below and given here again: [177933905] ASSERT(0) at CheckNUpdateCHTableByVif() in umac/umac_s1g_channel.c, 1033 or [Error] CC is 00 or 99. Skip loading BD and setting CC
It is mandatory to set the regulatory domain every boot: (example shows for USA)
iw reg set US
- Verify the cli_app can talk to the GW16146 module:
# cli_app show version Newracom Firmware Version : 01.05.00 gerrit/master : 69f978e OK
- Device sleeping
Be sure the regulatory domain is set as describe above and the interface is brought up afterwards with the following command:
[Error] the target device cannot respond while deep sleep.
ifconfig wlan0 up #assuming wlan0 is your GW16146
Hardware
The Mini-PCIe connector on the GW16146 uses the USB channel only for communicating to the 802.11ah module. See below schematic for the connector.
J1 Test Debug Header
J1 is a header that is not loaded by default but can be loaded on 100 piece or more orders.
This header can allow for a direct UART connection to the SX-NEWAH chip.
| Pin | Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3VDC |
| 2 | MODE |
| 3 | UART_TX |
| 4 | UART_RX |
| 5 | Ground |
Attachments (7)
- gw16146v3.png (620.3 KB ) - added by 4 years ago.
- 80211ahadvantages.png (133.0 KB ) - added by 4 years ago.
-
GW16146.sh
(855 bytes
) - added by 4 years ago.
GW16145 configuration script
-
GW16146_pinout.png
(417.9 KB
) - added by 4 years ago.
Mini-PCIe Schematic
- j1gw16146.png (30.5 KB ) - added by 2 years ago.
- silexantennas.png (91.1 KB ) - added by 2 years ago.
- silex-halow-countries.png (588.7 KB ) - added by 19 months ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip