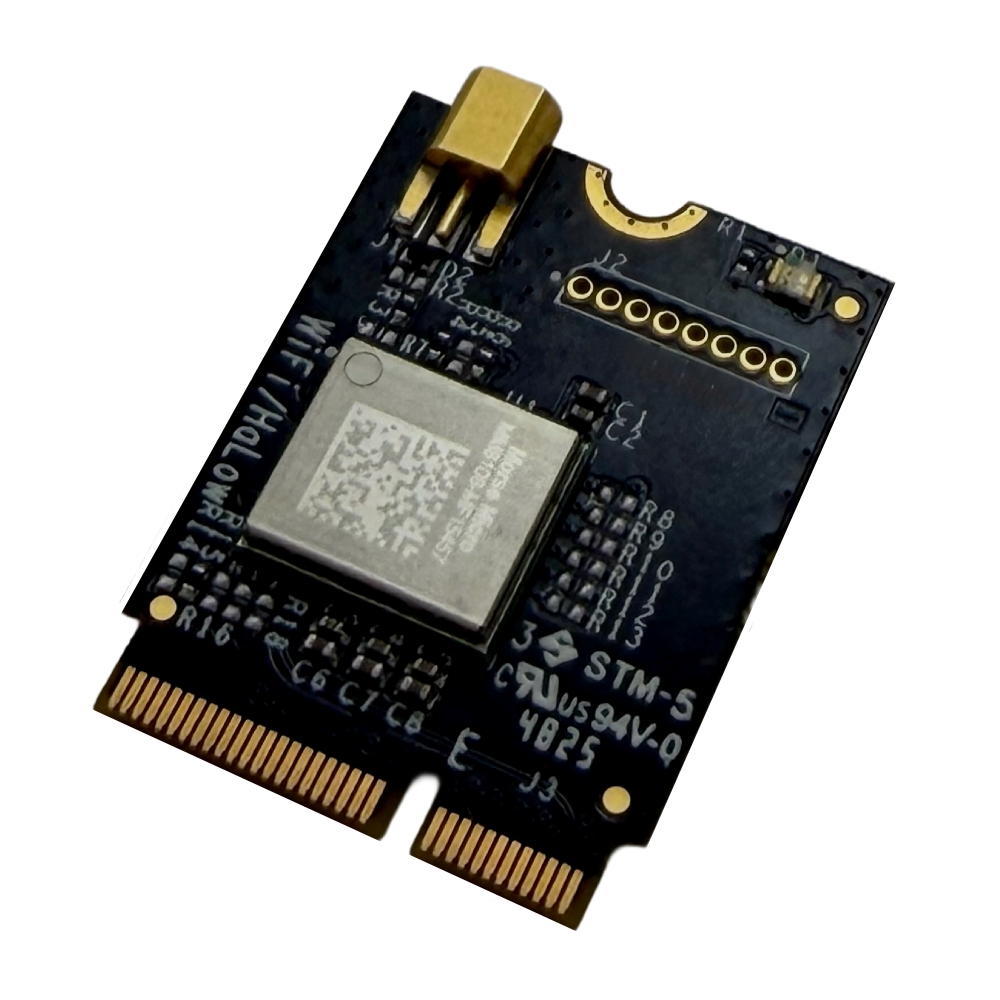
GW16167 M.2 E-Key 802.11ah (HaLow) 900MHz Radio
The GW16167 M.2 E-Key Sub-1GHz 802.11ah radio uses the second-generation MorseMicro MM8108 chip which offers improvements in range and throughput (up to 43.33Mbps) over the first generation MM6108.
* NOTE: The GW16167 has been tested and is supported in software when using a Gateworks Single Board Computer
* NOTE: The GW16167 requires an M.2 E-Key socket with USB 2.0. This may require an adapter for the Venice SBCs such as the GW16151
* NOTE: The GW16167 requires an updated driver and driver configuration present in the latest Gateworks pre-built Ubuntu and OpenWrt images - please update your firmware to ensure you have the proper support
IEEE 802.11ah is a wireless networking protocol published in 2017 called Wi-Fi HaLow as an amendment of the IEEE 802.11-2007 wireless networking standard. It uses 900 MHz license-exempt bands to provide extended-range Wi-Fi networks, compared to conventional Wi-Fi networks operating in the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands. It also benefits from lower energy consumption, allowing the creation of large groups of stations or sensors that cooperate to share signals, supporting the concept of the Internet of things (IoT). The protocol's low power consumption competes with Bluetooth, LoRa, and Zigbee, and has the added benefit of higher data rates and wider coverage range.
The radio communicates over the USB 2.0 bus
Datasheets:
WiFi Details:
- WiFi HaLow 802.11ah 850-950MHz bands 1/2/4/8MHz channel width 26dBm max output power and 43.3Mbps theoretical maximum transmission rate
Software Details:
- Required software:
- Out-of-tree kernel driver: https://github.com/Gateworks/morse_driver/tree/gateworks-venice (forked from https://github.com/MorseMicro/morse_driver.git)
- Firmware: https://github.com/MorseMicro/morse-firmware.git
- Required CLI app: https://github.com/MorseMicro/morse_cli.git
- Custom version of hostapd/wpa_supplicant: https://github.com/MorseMicro/hostap
M.2 Pinout
Gateworks follows the wider M.2 spec for E-Key signalling.
M.2 Pin Details:
- M2.2: 3.3VDC
- M2.3: USB+
- M2.4: 3.3VDC
- M2.5: USB-
- M2.56: W_DISABLE1# routed to the RESET_N pin of the MM8108 module a 200k pu to VDD_3P3
- M2.54: W_DISABLE2# routed to the WAKE pin of the MM8108 module with a 10k pu to VDD_3P3
- M2.72: 3.3VDC
- M2.74: 3.3VDC
- M.2 various pins GND, per M.2 E-Key Spec (such as 1,7, 33,39,45,51,57,63,69,75)
Antenna
The antenna port is MMCX, 50 ohms impedance.
The FCC cert from MorseMicro module uses a specific antenna that has a 1dBi gain.
The certified antenna is:
- Pulse W1063/ W1063M
- Freq : 902-928 gain: 1.00 dBi
- The two part variants are just different connector types (RPSMA/SMA).
- Example link: Digi-Key
Note, a pigtail, MMCX to RPSMA will be needed with the above antenna..
Note, using other dipole antennas in the 902-928 mhz with a 1.0 dBi gain should be supported for certification, but verify with a testing lab.
Certifications
The MM8108-MF15457 from MorseMicro has modular certifications at the following:
- FCC Part 15
- FCC ID: 2A74O-737B5B
- IC (Canada)
- 29791-737B5B
Note, these certifications are only with the antennas used in certification or with the same specification as noted in the #antenna section on this page.
Note, while the module may be certified, often the final entire product (SBC, power supply, wireless cards, enclosure) have to be put through a final certification.
Europe Use
This radio is a global radio and can be used in Europe, however, Europe has more restrictions with a summary below.
EU restrictions:
- Channels: 1 MHz and 2 Mhz channels only
- Duty cycle: 10% for AP, 2.8% for STA (measure over an hour). Can transmit for 360 seconds every hour as an AP, 100 seconds per hour as STA
- Power:
- 16.13 dBm EIRP for non audio video
- 12 dBm EIRP without duty cycling requirement for certain audio & video applications (EU Decision 2022/180)
Notes:
- The firmware will try to spread transmissions out across the hour
- There is a burst mode too that allows full throughput up to duty cycle. Caveat, on AP there is a slight reduction to allow for beacons across the hour
- Setting the country code as EU or UK in firmware (config store), will impose these restrictions. A One time programmable fuse can also be set to ensure compliance.
Software
Note: The GW16167 is designed to be used with a Gateworks Single Board Computer. When using the device on other platforms, Gateworks has limited knowledge and the support offered is being able to point to the Gateworks driver github link here: https://github.com/Gateworks/morse_driver (use the 1.16.4-gateworks branch)
Pre-Built Software Images
The MM8108 driver from MorseMicro is supported in our latest pre-built images for the Gateworks Single Board Computers. If using a SBC with software already installed, it is important to install the very latest from the dev.gateworks.com server below:
- noble-venice.img.gz (see compressed-disk-image)
- linux-venice.tar.xz Kernel tarball (see kernel-tarball install)
- OpenWrt - See #openwrt
Driver
The MM8108 on the GW16167 is supported by the open-source out-of-tree Linux kernel driver from MorseMicro. This driver is included in the Gateworks Ubuntu pre-built images and the below instructions are only for if building is needed. Note, this pulls from multiple repos, including the Gateworks Github where the 1.16.4-gateworks branch should be used.
Building with the Gateworks Venice BSP:
- Add a 'custom_kernel_morsemicro' script
cat <<\EOF > custom_kernel_morsemicro #!/bin/bash -e DIR=$PWD/mm610x OUTDIR=$DIR/out DESTDIR=$2 MORSE_VER=1.16.4 LIBNL_VER=libnl3_11_0 OPENSSL_VER=openssl-3.5.0 LIBUSB_VER=v1.0.28 COUNTRY=US mkdir -p $DESTDIR/usr/sbin mkdir -p $DESTDIR/etc/modprobe.d mkdir -p $DIR cd $DIR # get repos of what we will build [ -d morse_driver ] || git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/Gateworks/morse_driver.git -b 1.16.4-gateworks [ -d morse-firmware ] || git clone https://github.com/MorseMicro/morse-firmware.git -b 1.16 [ -d libnl ] || git clone https://github.com/thom311/libnl.git -b $LIBNL_VER [ -d openssl ] || git clone https://github.com/openssl/openssl.git -b $OPENSSL_VER [ -d hostap ] || git clone https://github.com/MorseMicro/hostap.git -b $MORSE_VER [ -d morse_cli ] || git clone https://github.com/MorseMicro/morse_cli.git -b $MORSE_VER [ -d libusb ] || git clone https://github.com/libusb/libusb.git -b $LIBUSB_VER echo "Building morse_driver..." ARGS="KERNEL_SRC=$1 \ CONFIG_MORSE_SDIO=y \ CONFIG_MORSE_USB=y \ CONFIG_MORSE_USER_ACCESS=y \ CONFIG_MORSE_VENDOR_COMMAND=y \ CONFIG_MORSE_SDIO_ALIGNMENT=4 \ CONFIG_MORSE_POWERSAVE_MODE=0 \ CONFIG_MORSE_COUNTRY=$COUNTRY \ CONFIG_MORSE_RC=y \ CONFIG_MORSE_MONITOR=y \ CONFIG_MORSE_DEBUGFS=y \ CONFIG_WLAN_VENDOR_MORSE=m" make -C morse_driver $ARGS make -C morse_driver $ARGS INSTALL_MOD_PATH=$2 modules_install # firmware: # - mm610x firmware # - board configuration file (BCF) that provides driver with calibration constants and chip gpio config echo "Copying firmware..." mkdir -p $2/lib/firmware/morse # GW16159 sdmah/sdio/mm6108 cp morse-firmware/firmware/mm6108.bin $2/lib/firmware/morse wget http://dev.gateworks.com/firmware/gw16159/$MORSE_VER/LICENSE -O $2/lib/firmware/morse/LICENSE wget "http://dev.gateworks.com/firmware/gw16159/$MORSE_VER/bcf_default.bin" -O $2/lib/firmware/morse/bcf_default.bin # GW16167 mm8108/usb cp morse-firmware/firmware/mm8108b2-rl.bin $2/lib/firmware/morse cp -P morse-firmware/bcf/morsemicro/* $2/lib/firmware/morse [ -d $OUTDIR/include/libnl3 ] || { echo "Building libnl..." cd libnl ./autogen.sh ./configure --host=$ARCH CC=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc --prefix=$OUTDIR --disable-shared make clean make -j$(nproc) make install cd .. } [ -d $OUTDIR/include/openssl ] || { echo "Building openssl..." cd openssl ./Configure linux-generic32 no-shared no-dso no-async -DL_ENDIAN --prefix=$OUTDIR --openssldir=$OUTDIR # needed no-async to build latest openssl against uclib make -j$(nproc) \ CC=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc \ RANLIB=${CROSS_COMPILE}ranlib \ LD=${CROSS_COMPILE}ld \ MAKEDEPPROG=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc \ PROCESSOR=ARM #make install # installs man pages too make install_sw cd .. } # libusb [ -d $OUTDIR/include/libusb ] || { echo "Building libusb..." cd libusb ./autogen.sh --disable-udev ./configure --host=$ARCH CC=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc --prefix=$OUTDIR --disable-shared --enable-examples-build --disable-log --disable-udev make -j$(nproc) \ CFLAGS="-Wunused-parameter" \ CC=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc \ RANLIB=${CROSS_COMPILE}ranlib \ LD=${CROSS_COMPILE}ld \ MAKEDEPPROG=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc \ PROCESSOR=ARM make install cd .. } # wpa_supplicant [ -r hostap/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant_s1g ] || { echo "Building wpa_supplicant_s1g..." cp hostap/wpa_supplicant/defconfig hostap/wpa_supplicant/.config disables="CONFIG_BGSCAN_SIMPLE" enables="CONFIG_DRIVER_NL80211_QCA \ CONFIG_WPS_NFC CONFIG_SAE_PK \ CONFIG_EAP_MD5 \ CONFIG_EAP_MSCHAPV2 \ CONFIG_EAP_TLS \ CONFIG_EAP_TLSV1_3 \ CONFIG_EAP_PEAP \ CONFIG_EAP_TTLS \ CONFIG_EAP_GTC \ CONFIG_EAP_PWD \ CONFIG_WPS_ER \ CONFIG_WPS_REG_DISABLE_OPEN \ CONFIG_WPS_NFC \ CONFIG_SAE_PK \ CONFIG_DEBUG_SYSLOG_FACILITY \ CONFIG_MESH \ CONFIG_BGSCAN_SIMPLE \ " for opt in $enables; do sed -i -e "s/^#$opt=y/$opt=y/" hostap/wpa_supplicant/.config done for opt in $disables; do sed -i -e "s/^$opt=y/#$opt=y/" hostap/wpa_supplicant/.config done make -C hostap/wpa_supplicant/ clean PKG_CONFIG_PATH="$OUTDIR/lib/pkgconfig" \ CFLAGS="-D_GNU_SOURCE -I $OUTDIR/include/libnl3 -I $OUTDIR/include -Wno-deprecated-declarations" \ LDFLAGS="-L $OUTDIR/lib/ --static" \ DESTDIR="$OUTDIR/sbin" \ BINDIR=/usr/sbin \ LIBS="-lnl-3 -lm -lpthread -lcrypto -lssl" \ CC=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc \ make -j$(nproc) -C hostap/wpa_supplicant/ } cp hostap/wpa_supplicant/{wpa_supplicant_s1g,wpa_cli_s1g,wpa_passphrase_s1g} $DESTDIR/usr/sbin/ # hostapd [ -r hostap/hostapd/hostapd_s1g ] || { echo "Building hostapd_s1g..." cp hostap/hostapd/defconfig hostap/hostapd/.config disables="" enables="CONFIG_DRIVER_NL80211_QCA \ CONFIG_EAP \ CONFIG_EAP_MD5 \ CONFIG_EAP_EKE \ CONFIG_EAP_MSCHAPV2 \ CONFIG_EAP_PEAP \ CONFIG_EAP_TLS \ CONFIG_EAP_TTLS \ CONFIG_EAP_GTC \ CONFIG_EAP_SIM \ CONFIG_EAP_AKA \ CONFIG_EAP_AKA_PRIME \ CONFIG_EAP_PAX \ CONFIG_EAP_PSK \ CONFIG_EAP_PWD \ CONFIG_EAP_SAKE \ CONFIG_EAP_GPSK \ CONFIG_EAP_GPSK_SHA256 \ CONFIG_EAP_FAST \ CONFIG_EAP_TEAP \ CONFIG_WPS \ CONFIG_WPS_UPNP \ CONFIG_WPS_NFC \ CONFIG_EAP_IKEV2 \ CONFIG_EAP_TNC \ CONFIG_RADIUS_SERVER \ CONFIG_SAE \ CONFIG_SAE_PK \ CONFIG_TLSV11 \ CONFIG_TLSV12 \ " for opt in $enables; do sed -i -e "s/^#$opt=y/$opt=y/" hostap/hostapd/.config done for opt in $disables; do sed -i -e "s/^$opt=y/#$opt=y/" hostap/hostapd/.config done make -C hostap/hostapd/ clean PKG_CONFIG_PATH="$OUTDIR/lib/pkgconfig" \ CFLAGS="-D_GNU_SOURCE -I $OUTDIR/include/libnl3 -I $OUTDIR/include -Wno-deprecated-declarations" \ LDFLAGS="-L $OUTDIR/lib/ --static" \ DESTDIR="$OUTDIR/sbin" \ BINDIR=/usr/sbin \ LIBS="-lnl-3 -lm -lpthread -lcrypto -lssl" \ CC=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc \ make -j$(nproc) -C hostap/hostapd/ } cp hostap/hostapd/{hostapd_s1g,hostapd_cli_s1g} $DESTDIR/usr/sbin/ # morse_cli [ -r morse_cli/morse_cli.bin ] || { echo "Building morse_cli..." make -C morse_cli clean PKG_CONFIG_PATH="$OUTDIR/lib/pkgconfig" \ CFLAGS="-I $OUTDIR/include/libnl3 -I $OUTDIR/include/libusb-1.0 -I $OUTDIR/include" \ LDFLAGS="-L $OUTDIR/lib/ --static" \ CC=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc \ make \ CONFIG_MORSE_TRANS_NL80211=1 \ CONFIG_MORSE_STATIC=1 \ -j$(nproc) -C morse_cli } cp morse_cli/morse_cli $DESTDIR/usr/sbin/ # module parameters echo "options morse country=$COUNTRY enable_ext_xtal_init=1" > $DESTDIR/etc/modprobe.d/morse.conf EOF chmod +x custom_kernel_morsemicro
- rebuild the ubuntu-image:
source ./setup-environment make ubuntu-image
Module Parameters:
- There are a number of module parameters supported by morse.ko however the required ones for the GW16167 are:
- country=US
- These can be placed in /etc/modprobe..d such as:
echo "options morse country=US" > /etc/modprobe.d/morse.conf
- Note that our build example and pre-built BSP's also add a 'enable_ext_xtal_init=1' which is not needed for the USB based GW16167 but is needed for the SDIO based GW16159 as it has an external XTAL; we add it so that both cards are supported
Console Messages:
# lsusb | grep Morse Bus 003 Device 003: ID 325b:8100 Morse Micro MM81xx Wi-Fi HaLow 802.11ah Transceiver # dmesg | grep morse # dmesg | grep morse [ 8.298087] morse micro driver registration. Version v1.16.4-gdec5bc215b88 [ 8.298612] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: USB Morse device now attached to Morse driver (minor=-1) [ 8.312450] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: Loaded firmware from morse/mm8108b2-rl.bin, size 456924, crc32 0xe4799c8d [ 8.313800] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: Loaded BCF from morse/bcf_boardtype_0807.bin, size 2081, crc32 0xa80ae47b [ 9.451353] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: morse_mac_init: WARNING enable_ps modparam must only be used for testing - use iw set power_save [ 9.524340] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: Driver loaded with kernel module parameters [ 9.524372] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: slow_clock_mode : 0 [ 9.524407] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_1mhz_probes : Y [ 9.524416] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_sched_scan : Y [ 9.524424] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_hw_scan : Y [ 9.524432] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_pv1 : N [ 9.524440] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_page_slicing : N [ 9.524448] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: log_modparams_on_boot : Y [ 9.524455] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_mcast_rate_control : N [ 9.524463] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_mcast_whitelist : Y [ 9.524471] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: ocs_type : 1 [ 9.524479] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_wiphy : N [ 9.524487] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_auto_mpsw : Y [ 9.524493] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: duty_cycle_probe_retry_threshold : 2500 [ 9.524499] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: duty_cycle_mode : 0 [ 9.524504] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_auto_duty_cycle : Y [ 9.524511] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: dhcpc_lease_update_script : /morse/scripts/dhcpc_update.sh [ 9.524517] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_ibss_probe_filtering : Y [ 9.524526] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_dhcpc_offload : N [ 9.524533] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_arp_offload : N [ 9.524541] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_bcn_change_seq_monitor : N [ 9.524549] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_cac : N [ 9.524555] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: max_mc_frames : 10 [ 9.524564] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: tx_max_power_mbm : 2200 [ 9.524572] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_twt : Y [ 9.524580] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_mac80211_connection_monitor : N [ 9.524588] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_airtime_fairness : N [ 9.524596] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_raw : Y [ 9.524604] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: max_aggregation_count : 0 [ 9.524612] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: max_rate_tries : 1 [ 9.524620] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: max_rates : 4 [ 9.524627] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_watchdog_reset : N [ 9.524635] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: watchdog_interval_secs : 30 [ 9.524643] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_watchdog : Y [ 9.524651] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: country : US [ 9.524659] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_cts_to_self : N [ 9.524667] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_rts_8mhz : N [ 9.524674] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_trav_pilot : Y [ 9.524682] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_sgi_rc : Y [ 9.524689] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_mbssid_ie : N [ 9.524697] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: virtual_sta_max : 0 [ 9.524705] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: thin_lmac : N [ 9.524712] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_dynamic_ps_offload : Y [ 9.524720] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_ps : 0 [ 9.524728] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_subbands : 2 [ 9.524736] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_survey : Y [ 9.524744] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: mcs10_mode : 0 [ 9.524750] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: mcs_mask : 1023 [ 9.524755] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: no_hwcrypt : N [ 9.524761] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_ext_xtal_init : Y [ 9.524767] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_otp_check : Y [ 9.524772] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: bcf : [ 9.524781] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: serial : default [ 9.524788] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: debug_mask : 8 [ 9.524796] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: tx_status_lifetime_ms : 15000 [ 9.524805] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: tx_queued_lifetime_ms : 1000 [ 9.524813] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: max_txq_len : 32 [ 9.524821] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: default_cmd_timeout_ms : 600 [ 9.524829] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: reattach_hw : N [ 9.524838] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: hw_reload_after_stop : 5 [ 9.524846] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_short_bcn_as_dtim_override : -1 [ 9.524852] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: fw_bin_file : [ 9.524868] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: sdio_reset_time : 400 [ 9.524877] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: macaddr_suffix : 00:00:00 [ 9.524885] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: macaddr_octet : 255 [ 9.524893] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: max_total_vendor_ie_bytes : 514 [ 9.524902] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: coredump_include : 1 [ 9.524910] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: coredump_method : 1 [ 9.524917] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_coredump : Y [ 9.524925] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: sdio_clk_debugfs : [ 9.524933] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_mm_vendor_ie : Y [ 9.524941] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: fixed_guard : 0 [ 9.524949] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: fixed_ss : 1 [ 9.524956] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: fixed_bw : 2 [ 9.524964] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: fixed_mcs : 4 [ 9.524972] morse_usb 3-1.2:1.0: enable_fixed_rate : N [ 9.527922] morse_io: Device node '/dev/morse_io' created successfully [ 9.528089] usbcore: registered new interface driver morse_usb # ls -l /sys/class/net/wlan0 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 21 23:05 /sys/class/net/wlan0 -> ../../devices/platform/soc@0/32f10108.usb/38200000.usb/xhci -hcd.1.auto/usb3/3-1/3-1.2/3-1.2:1.0/net/wlan0
hostapd and wpa_supplicant
MorseMicro has a custom version of hostapd and wpa_supplicant with support added for 802.11ah. For most of the added configuration options there is no current way to pass them via ieee80211 APIs with nl80211 so instead the configuration is supplied via vendor-specific commands using the morse_cli userspace application. These are typically built as hostapd_s1g and wpa_supplicant_s1g so that they can coexist with the standard tools. These commands are being used in the access point and station examples further down on this wiki page.
morse_cli
The morse_cli userspace application can be used to interact with the driver. It communicates over netlink so the interface must be up before you can talk to it. Much of the functionality is present for hostapd_s1g and wpa_supplicant_s1g to use.
Examples:
# make sure interface is up ifconfig wlan0 up # morse_cli --interface=wlan0 hw_version HW Version: MM8108 # morse_cli --interface=wlan0 version Morse_cli Version: rel_1_12_5_2024_Jul_25-4-g3541610 FW Version: rel_1_12_4_2024_Jun_11 # morse_cli channel Full Channel Information Operating Frequency: 916000 kHz Operating BW: 8 MHz Primary BW: 2 MHz Primary Channel Index: 0
- note if not specified the interface defaults to wlan0
Kernel Patches
There is a small set of kernel patches from MorseMicro which may improve the experience for 802.11ah for specific use cases. Gateworks has found these patches to be unnecessary for most use cases including AP, STA, and 802.11s MESH. These patches from MorseMicro exist for several LTS kernels at https://github.com/MorseMicro/linux
Here is an evaluation of the various patches for a 6.6 kernel:
- mac80211: implement support for thin LMAC S1G NDP block acknowledgements
- this is necessary if you are using the think LMAC firmware (which we have found no documentation on)
- mac80211: Mesh support
- MESH improvements
- mac80211: IBSS bridge support
- this is necessary if you are using the old IBSS/Adhoc mode in a bridge (not required for 802.11S MESH)
- mac80211: tx s1g AP ecsa support
- powersave enhancement
- mac80211: mlme s1g ecsa support
- powersave enhancement
A basic AP/station HaLow network without powersave requirements or extended channel switch will function without these patches.
It has been reported that with these kernel patches have not caused any noticeable obvious issues with other mac80211 radios
OpenWrt
Support has been added for the GW16167 to the Gateworks OpenWrt packages for the 24.10/25.12 branches:
- https://github.com/Gateworks/gw-openwrt-packages/tree/24.10/gateworks/morse-micro
- https://github.com/Gateworks/gw-openwrt-packages/tree/25.12/gateworks/morse-micro
The morse_driver and morse-fw packages are required and included in the pre-built Gateworks OpenWrt image for venice: https://dev.gateworks.com/venice/images/openwrt-venice.img.gz OpenWrt will recognize the interface as a generic 5Ghz radio and allow you to configure it as an AP or a STA. OpenWrt does not understand that the channels map to the sub-1GHz band. The bandwidths will map as follows:
- 20MHz = 1MHz sub-1G
- 40MHz = 2MHz sub-1G
- 80MHz = 4MHz sub-1G
- 160MHz = 8MHz sub-1G
Please note that WiFi interfaces do not appear in /sys/class/net in OpenWrt.
For testing HaLow AP/STA/Mesh, Gateworks currently recommends avoiding the OpenWrt UCI layer for configuration of the interface, as it is not yet fully compatible with all features (i.e. WPA3 setup) out-of-the-box. Instead, a reliable approach is to have UCI not configure the HaLow radio/interface, and manually set it up via the s1g tools (wpa_supplicant_s1g, hostapd_s1g), explained in the Configuration section below. This route still allows for UCI / LuCI GUI to be used to configure other interfaces, bridges, etc. depending on your intended goal.
# Disable UCI’s wifi control for radio0 (gw16167) uci set wireless.radio0.disabled='1' uci commit wireless # Potentially setup firewall zones here # Setup interface manually # i.e. iw phy phy0 interface add wlan0 type managed ifconfig wlan0 up # For quick testing, allow incoming traffic /etc/init.d/firewall stop # Now bring up network with hostapd_s1g or wpa_supplicant_s1g
Note: By default, the OpenWrt firewall will block incoming data from wlan0 as /etc/config/firewall does not assign it into a zone. For testing, you can stop and disable the firewall, or configure it properly according to the OpenWrt firewall documentation.
Channel Mapping
The HaLow channels are mapped to standard 802.11 channels:
- US
| S1G Op Class | Global Op Class | Channel Bandwidth | HaLow Channel Number | Center Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 1 | 902.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 3 | 903.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 5 | 904.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 7 | 905.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 9 | 906.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 11 | 907.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 13 | 908.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 15 | 909.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 17 | 910.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 19 | 911.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 21 | 912.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 23 | 913.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 25 | 914.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 27 | 915.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 29 | 916.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 31 | 917.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 33 | 918.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 35 | 919.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 37 | 920.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 39 | 921.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 41 | 922.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 43 | 923.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 45 | 924.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 47 | 925.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 49 | 926.5 |
| 1 | 68 | 1 | 51 | 927.5 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 2 | 903.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 6 | 905.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 10 | 907.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 14 | 909.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 18 | 911.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 22 | 913.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 26 | 915.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 30 | 917.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 34 | 919.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 38 | 921.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 42 | 923.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 46 | 925.0 |
| 2 | 69 | 2 | 50 | 927.0 |
| 2 | 70 | 4 | 8 | 906.0 |
| 2 | 70 | 4 | 16 | 910.0 |
| 2 | 70 | 4 | 24 | 914.0 |
| 2 | 70 | 4 | 32 | 918.0 |
| 2 | 70 | 4 | 40 | 922.0 |
| 2 | 70 | 4 | 48 | 926.0 |
| 2 | 71 | 8 | 12 | 908.0 |
| 2 | 71 | 8 | 28 | 916.0 |
| 2 | 71 | 8 | 44 | 924.0 |
To see what frequency the radio is configured for, use the following command and example with channel=28 and op_class=71 in the host ap conf file:
root@OpenWrt:~# morse_cli channel Full Channel Information Operating Frequency: 916000 kHz Operating BW: 8 MHz Primary BW: 2 MHz Primary Channel Index: 0 root@OpenWrt:~#
Note, some OS's will report the HaLow radio working over 5GHz due to the standard WiFi not being aware of sub-1GHz.
There are times that Linux can recognize the interface as a generic 5Ghz radio and allow you to configure it as an AP or a STA. Linux does not understand that the channels map to the sub-1GHz band. The bandwidths will map as follows:
- 20MHz = 1MHz sub-1G
- 40MHz = 2MHz sub-1G
- 80MHz = 4MHz sub-1G
- 160MHz = 8MHz sub-1G
Example with channel=28 and op_class=71 in the host ap conf file::
root@OpenWrt:~# iw dev wlan0 info Interface wlan0 ifindex 9 wdev 0x1 addr 0c:bf:74:00:27:10 ssid HaLow-WPA2 type AP wiphy 0 channel 100 (5500 MHz), width: 160 MHz, center1: 5570 MHz txpower 20.00 dBm multicast TXQ: qsz-byt qsz-pkt flows drops marks overlmt hashcol tx-bytes tx-packets 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Configuration (AP, STA, Mesh)
The changes made by MorseMicro to hostap add a number of parameters to hostapd.conf:
- ieee80211ah: IEEE 802.11ah (S1G) supported
- s1g_prim_chwidth: Sub-1 GHz primary channel (used for control/management signalling) within the wider bonded channel: 0=1Mhz, 1=2MHz
- s1g_prim_1mhz_chan_index: Sub-1 GHz primary 1MHz channel index used to refine the selection of the primary channel within the the operating channel by s1g_prim_chwidth: 0 for 1Mhz, 0-1 for 2Mhz, 0-3 for 4Mhz, 0-7 for 8MHz
- s1g_capab: S1G capabilities (list of flags)
- s1g_traveling_pilots: Sub-1 Ghz traveling pilots
- s1g_bss_color: Sub-1 GHz BSS color (0-7).
- s1g_max_mpdu: Sub-1 GHz MPDU maximum length
- s1g_ampdu: Sub-1 GHz A-MPDU support
- s1g_max_ampdu_len_exp: Sub-1 GHz A-MPDU length exponent
- s1g_basic_mcs_nss_set: Sub-1 GHz basic NSS/MCS support
For documentation on these refer to the code:
Below are examples for configuring WPA2/WPA3 AP + STA, along with WPA3 Mesh.
AP & STA
- Infrastructure mode using WPA2:
- AP:
cat << EOF > hostapd_s1g_wpa2.conf interface=wlan0 logger_syslog=-1 logger_syslog_level=2 logger_stdout=-1 logger_stdout_level=2 ctrl_interface=/var/run/hostapd ctrl_interface_group=0 ssid=HaLow-WPA2 country_code=US hw_mode=a beacon_int=100 dtim_period=10 max_num_sta=255 rts_threshold=-1 fragm_threshold=-1 macaddr_acl=0 auth_algs=3 ignore_broadcast_ssid=0 wmm_enabled=1 wmm_ac_bk_cwmin=4 wmm_ac_bk_cwmax=10 wmm_ac_bk_aifs=7 wmm_ac_bk_txop_limit=0 wmm_ac_bk_acm=0 wmm_ac_be_aifs=3 wmm_ac_be_cwmin=4 wmm_ac_be_cwmax=10 wmm_ac_be_txop_limit=0 wmm_ac_be_acm=0 wmm_ac_vi_aifs=2 wmm_ac_vi_cwmin=3 wmm_ac_vi_cwmax=4 wmm_ac_vi_txop_limit=94 wmm_ac_vi_acm=0 wmm_ac_vo_aifs=2 wmm_ac_vo_cwmin=2 wmm_ac_vo_cwmax=3 wmm_ac_vo_txop_limit=47 wmm_ac_vo_acm=0 ieee80211ah=1 s1g_capab=[SHORT-GI-ALL] eapol_key_index_workaround=0 own_ip_addr=127.0.0.1 # 1MHz@918.5MHz #channel=33 #op_class=68 # 2MHz@907MHz #channel=10 #op_class=69 # 4MHz@922MHz #channel=40 #op_class=70 # 8MHz@916MHz channel=28 op_class=71 s1g_prim_chwidth=1 s1g_prim_1mhz_chan_index=0 # WPA2 security wpa=2 wpa_passphrase=strongpassword123 wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK wpa_pairwise=TKIP rsn_pairwise=CCMP EOF hostapd_s1g ./hostapd_s1g_wpa2.conf -B #-B needs to be after the command in OpenWrt ifconfig wlan0 192.168.1.1 iperf3 -s
- STA:
#wpa_passphrase generates WPA2 wpa_supplicant configuration wpa_passphrase_s1g HaLow-WPA2 strongpassword123 > wpa_supplicant_s1g_wpa2.conf #ensure wlan0 interface is up ifconfig wlan0 up #Start wpa_supplicant_s1g, send to background (replace & with -d for debug) wpa_supplicant_s1g -i wlan0 -c ./wpa_supplicant_s1g_wpa2.conf & #assign static IP; DHCP is not part of this example ifconfig wlan0 192.168.1.128 iperf3 -c 192.168.1.1
- AP:
- Infrastructure mode using WPA3:
- AP:
cat << EOF > hostapd_s1g_wpa3.conf interface=wlan0 logger_syslog=-1 logger_syslog_level=2 logger_stdout=-1 logger_stdout_level=2 ctrl_interface=/var/run/hostapd ctrl_interface_group=0 ssid=HaLow-WPA3 country_code=US hw_mode=a beacon_int=100 dtim_period=10 max_num_sta=255 rts_threshold=-1 fragm_threshold=-1 macaddr_acl=0 auth_algs=3 ignore_broadcast_ssid=0 wmm_enabled=1 wmm_ac_bk_cwmin=4 wmm_ac_bk_cwmax=10 wmm_ac_bk_aifs=7 wmm_ac_bk_txop_limit=0 wmm_ac_bk_acm=0 wmm_ac_be_aifs=3 wmm_ac_be_cwmin=4 wmm_ac_be_cwmax=10 wmm_ac_be_txop_limit=0 wmm_ac_be_acm=0 wmm_ac_vi_aifs=2 wmm_ac_vi_cwmin=3 wmm_ac_vi_cwmax=4 wmm_ac_vi_txop_limit=94 wmm_ac_vi_acm=0 wmm_ac_vo_aifs=2 wmm_ac_vo_cwmin=2 wmm_ac_vo_cwmax=3 wmm_ac_vo_txop_limit=47 wmm_ac_vo_acm=0 ieee80211ah=1 s1g_capab=[SHORT-GI-ALL] eapol_key_index_workaround=0 own_ip_addr=127.0.0.1 #s1g_prim_chwidth=0 #s1g_prim_1mhz_chan_index=0 # 1MHz@918.5MHz #channel=33 #op_class=68 # 2MHz@907MHz #channel=10 #op_class=69 # 4MHz@922MHz #channel=40 #op_class=70 # 8MHz@916MHz #channel=28 #op_class=71 # WPA3 / SAE configuration wpa=2 wpa_key_mgmt=SAE ieee80211w=2 sae_pwe=2 rsn_pairwise=CCMP sae_password=HalowDemo123 EOF #Start the AP with configuration in background. #For quick (foreground) debugging, remove the -B flag hostapd_s1g ./hostapd_s1g_wpa3.conf -B #Configure static IP ifconfig wlan0 192.168.1.1 #Start iperf3 server for connection testing iperf3 -s
- STA:
#wpa_passphrase_s1g is only to create WPA2 configurations; create conf manually cat << EOF > wpa_supplicant_s1g_wpa3.conf update_config=1 pmf=2 sae_pwe=1 network={ ssid="HaLow-WPA3" key_mgmt=SAE pairwise=CCMP psk="strongpassword123" } EOF #Ensure interface is up ifconfig wlan0 up #Start wpa_supplicant_s1g, send to background (replace & with -d for debug) wpa_supplicant_s1g -i wlan0 -c ./wpa_supplicant_s1g_wpa3.conf & #Configure static IP, as dhcp is not present in example. ifconfig wlan0 192.168.1.128 iperf3 -c 192.168.1.1
- AP:
Mesh
- 802.11s Mesh using WPA3:
cat << EOF > wpa_supplicant_s1g_mesh_wpa3.conf country=US ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant_s1g sae_pwe=1 max_peer_links=10 mesh_fwding=1 network={ ssid="HaLow-WPA3-Mesh" key_mgmt=SAE mode=5 s1g_prim_chwidth=0 s1g_prim_1mhz_chan_index=0 # 1MHz@918.5MHz #channel=33 #op_class=68 # 2MHz@907MHz #channel=10 #op_class=69 # 4MHz@922Mhz #channel=40 #op_class=70 # 8MHz@916MHz channel=28 op_class=71 country="US" mesh_rssi_threshold=-85 sae_password="strongpassword123" pairwise=CCMP ieee80211w=2 beacon_int=1000 # 1.16.4 wpa_supplicant/mesh.c needs this set to 1 dtim_period=1 } EOF ifconfig wlan0 up wpa_supplicant_s1g -iwlan0 -c wpa_supplicant_s1g_mesh_wpa3.conf &
- Note: wpa_supplicant_s1g automatically configures the interface type from 'managed' to 'mesh point' when configured for mesh. It is cleaner practice and recommended for production systems, to setup the interface as a mesh point explicitly.
#optional: delete wlan0 interface iw dev wlan0 del iw phy phy0 interface add mesh0 type mp #morse_cli sanity check #morse_cli requires interface to talk to the driver; ensure interface is up ifconfig mesh0 up #morse_cli defaults to wlan0, so to use it we need to manually state -i mesh0 morse_cli -i mesh0 version
More information on mesh and 802.11s can be found on our mesh networks wiki page.
Thermal
While the MM8108 can operate from -40C to +85C. Currently, once the chip reaches 85C internally the transmitter is disabled to prevent damage. MorseMicro is exploring making this threshold configurable as well as options to implement a duty cycle or a reduced power mode instead of a full disable.
You can obtain the value of the internal temperature reading via morse_cli:
morse_cli -i wlan0 stats | grep Temp
Performance
The MM8108 supports:
- Spacial Streams: 1
- Channel bandwidths: 1/2/4/8 MHz
- Modulation and Coding Schemes: MCS 0-9 (1/2/4/8 Mhz); MCS 10 (1Mhz only)
- Data rates up to 43.33Mbps (MCS 9, 256-QAM, 8 Mhz channel, 4 us GI)
Since 802.11ah is designed for low-power, long-range IoT applications, its rates are lower than higher-frequency Wi-Fi standards like 802.11n/ac/ax.
802.11ah uses OFDM with a subcarrier spacing of 31.25 kHz (1/32 µs), scaled down from 802.11ac’s 312.5 kHz to support narrower channels. The number of data subcarriers varies with bandwidth:
- 1 MHz: 24 data subcarriers.
- 2 MHz: 52 data subcarriers.
- 4 MHz: 108 data subcarriers.
- 8 MHz: 234 data subcarriers.
The PHY rate is calculated as: PHY Rate = (Number of Data Subcarriers) × (Bits per Subcarrier) × (Coding Rate) × (Symbols per Second) × (Number of Spatial Streams):
- Data Subcarriers:
- 1 MHz: 24 data subcarriers.
- 2 MHz: 52 data subcarriers.
- 4 MHz: 108 data subcarriers.
- 8 MHz: 234 data subcarriers.
- Bits per Subcarier and Coding Rate: Depends on MCS index
- Symbols per Second:
- Long GI (8us): 4 us data + 4 us GI: 125,000 symbols/s
- Short GI (4us): 4 us data + 0 us GI: 250,000 symbols/s
- Spatial Streams: 1 (common for IoT devices).
Calculated max PHY Data Rates per MCS, channel bandwidth, and guard interval:
| MCS | Modulation | Coding rate | 1 MHz channel (Mbps) Long GI / Short GI | 2 MHz channel (Mbps) Long GI / Short GI | 4 MHz channel (Mbps) Long GI / Short GI | 8 MHz channel (Mbps) Long GI / Short GI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | BPSK | 1/2 | 0.3 / 0.33 | 0.65 / 0.72 | 1.35 / 1.5 | 2.925 / 3.25 |
| 1 | QPSK | 1/2 | 0.6 / 0.67 | 1.3 / 1.44 | 2.7 / 3.0 | 5.85 / 6.5 |
| 2 | QPSK | 3/4 | 0.9 / 1.0 | 1.95 / 2.17 | 4.05 / 4.5 | 8.775 / 9.75 |
| 3 | 16-QAM | 1/2 | 1.2 / 1.33 | 2.6 / 2.89 | 5.4 / 6.0 | 11.7 / 13.0 |
| 4 | 16-QAM | 3/4 | 1.8 / 2.0 | 3.9 / 4.33 | 8.1 / 9.0 | 17.55 / 19.5 |
| 5 | 64-QAM | 2/3 | 2.4 / 2.67 | 5.2 / 5.78 | 10.8 / 12.0 | 23.4 / 26.0 |
| 6 | 64-QAM | 3/4 | 2.7 / 3.0 | 5.85 / 6.5 | 12.15 / 13.5 | 26.3 / 29.3 |
| 7 | 64-QAM | 5/6 | 3.0 / 3.34 | 6.5 / 7.22 | 13.5 / 15.0 | 29.3 / 32.5 |
| 8 | 256-QAM | 3/4 | 3.6 / 4.0 | 7.8 / 8.667 | 16.20 / 18.0 | 35.1 / 39.0 |
| 9 | 256-QAM | 5/6 | N/A | 8.667 / 9.630 | 18.0 / 20.0 | 39.0 / 43.333 |
| 10 | BPSK | 1/2 | 0.15 / 0.17 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Note that MCS10 is a special case in 802.11ah and is for 1MHz cahnnels only with a repetition mode modulated with BPSK and 1/2 coding rate. This is for ultra-low rate extended range. The repetition doubles robustness but halves throughput.
Actual throughput will be less taking into account overhead, congestion, and RF factors. To examine your link you can use the following:
- examine the rate control stats:
cat /sys/kernel/debug/ieee80211/phy0/morse/mmrc_table
- examine your link status (RSSI and MCS info):
- AP:
iw dev wlan0 station dump
- STA:
iw dev wlan0 link
- AP:
The rate control stats /sys/kernel/debug/ieee80211/phy0/morse/mmrc_table will provide statistics from the Morse S1G TX Rate rate control algorithm:
- each line represents stats for a given channel bandwidth, guard band interval, and MCS index
- the 'rate_sel' column uses the following definitions:
- A : Highest throughput
- B : 2nd highest throughput
- C : baseline throughput
- P : Maximum delivery probability
- L : Used for additional lookarounds when traffic is very low
Examining this tells you what MCS rate you are using; if it is not the highest then look at RF characteristics such as antenna, transmit strength, RSSI, and interference.
Example:
- Using 8MHz Short GI:
# cat /sys/kernel/debug/ieee80211/phy0/morse/mmrc_table | head -n4; cat /sys/kernel/debug/ieee80211/phy0/morse/mmrc_table | grep 8MHz | grep SGI Morse Micro S1G RC Algorithm Statistics Peer: 0c:bf:74:00:27:62 --------------Rate-------------- Throughput Probability ---------Last--------- ---------Total--------- ----MPDU----- 8MHz SGI 0 C MCS0 1 7 3165 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8MHz SGI 0 MCS1 1 15 2122 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8MHz SGI 0 MCS2 1 23 1582 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8MHz SGI 0 MCS3 1 31 1043 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8MHz SGI 0 MCS4 1 39 791 19.50 19.49 100 0 0 0 3 3 0 0 8MHz SGI 0 MCS5 1 47 503 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8MHz SGI 0 MCS6 1 55 395 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8MHz SGI 0 P MCS7 1 63 323 32.50 32.49 100 0 0 0 878 885 0 0 8MHz SGI 0 B MCS8 1 71 287 39.00 36.26 93 0 0 0 1403 1462 0 0 8MHz SGI 0 A MCS9 1 79 251 46.79 46.36 96 0 0 0 43597 45721 0 0
- The above shows the majority of the packets are using MCS9, the highest rate for the mm8108.
Gateworks Testing Results (using WPA3 and iperf3):
- Infrastructure mode:
| Channel BW | Channel | op_class | Freq | TCP (mbps) | UDP (mbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1MHz | 33 | 68 | 918.5MHz | 3.25 | 3.63 |
| 2MHz | 10 | 69 | 907Mhz | 6.92 | 7.36 |
| 4MHz | 40 | 70 | 922Mhz | 15.2 | 16.0 |
| 8MHz | 28 | 71 | 916MHz | 26.0 | 29.8 |
- 802.11s Mesh
| Channel BW | Channel | op_class | Freq | TCP (mbps) | UDP (mbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1MHz | 33 | 68 | 918.5MHz | 2.94 | 3.53 |
| 2MHz | 10 | 69 | 907Mhz | 6.71 | 7.34 |
| 4MHz | 40 | 70 | 922Mhz | 15.4 | 16.2 |
| 8MHz | 28 | 71 | 916MHz | 26.7 | 30.4 |
Transmit Power
To see the tx power (txpower) use the command when the radio is active and note the txpower is at 20.00dBm:
root@noble-venice:~# iw dev wlan0 info Interface wlan0 ifindex 4 wdev 0x1 addr 0c:bf:74:cc:27:10 ssid HaLow-WPA2 type AP wiphy 0 channel 100 (5500 MHz), width: 160 MHz, center1: 5570 MHz txpower 20.00 dBm multicast TXQ: qsz-byt qsz-pkt flows drops marks overlmt hashcol tx-bytes tx-packets 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 root@noble-venice:~#
To set a different transmit power (txpower) use the line below for 9dBm (Note, it seems that the wlan0 interface needs to be taken down, any hostapd needs to be stopped, and then apply the setting, and bring back up the interface and restart hostapd):
root@noble-venice:~# iw dev wlan0 set txpower fixed 900
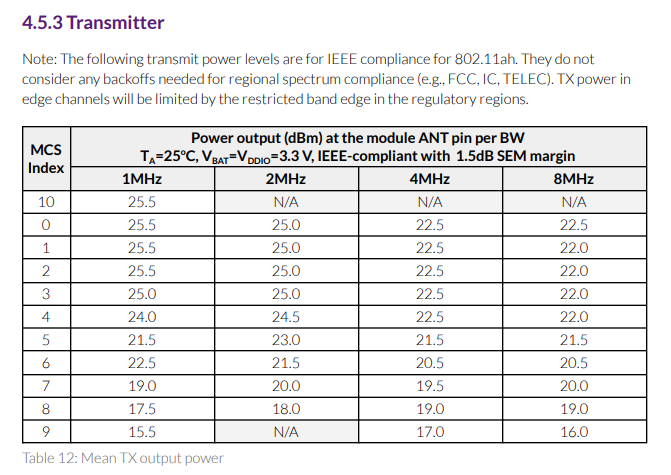
The module is rated to 26dBm max.
Please note this power output only happens at certain bandwidths and MCS indexes per the MM8108 datasheet in table 4.5.3 labeled Transmitter shown in the picture below:
Troubleshooting
- Be sure you are using the absolute latest software from dev.gateworks.com
- Be sure you see the device on the usb bus with the lsusb command:
lsusb 325b:8100 Morse Micro MM81xx Wi-Fi HaLow 802.11ah Transceiver
- If the device is not enumerating on the usb bus, then you should verify that your M.2 W_DISABLE1# (pin 56) and W_DISABLE2# (54) are logic high. Both of these pins have pull-up resistors on our card (200k for !W_DISABLE#1 and 10k for !W_DISABLE#2) so make sure you are not driving them low and do not have an on-board pull-down on your hardware.
- If you do not see the mm8108 enumerate on the USB bus, it could be that something is driving your PERST# signal low which would keep the mm8108 on the GW16167 in reset. You can verify this with a scope/meter on the PERST# signal.
- Verify with another card that USB 2.0 on the miniPCIe socket works.
- Be sure the output of command: dmesg | grep morse is a similar output to that in the driver section on this wiki page
- Install the latest Ubuntu software from dev.gateworks.com (Venice details here: venice/firmware
- For radio specific questions and driver questions, please reference the Morse Micro Community here: https://community.morsemicro.com/
GW11048-7 HaLow Dev Kit Quick Start
The GW16167 is sold in combination with a Gateworks GW7200 SBC and is called the GW11048-7 Development Kit.
This kit includes:
- GW7200 SBC
- GW16151 M.2 Adapter
- GW10174 Antenna
- GW10052 Antenna Adapter
Instructions:
- Mount the GW16167 radio onto the GW16151 M.2 adapter
- Mount this assembly in step 1 into either of the Mini-PCIe slots on the back of the GW7200 with supplied screws
- Connect the GW10052 antenna adapter to the antenna and then connect to the antenna port on the GW16167.
- The GW7200 in the kit comes pre-installed with Gateworks Ubuntu software that includes the GW16167 driver
- The GW16167 can be put into access point or station mode, per the directions in other sections on this wiki page. The GW16167 acts as a wireless card on the 802.11ah 900MHz band.
- To power on the SBC and get serial console access, follow the Gateworks general Quick Stage Page
For troubleshooting, see Troubleshooting section above
Attachments (2)
- GW16167_angled.jpg (294.1 KB ) - added by 5 weeks ago.
- tx.jpg (48.4 KB ) - added by 7 days ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip